SMT assembly lines are designed to handle the precise placement of tiny electronic components onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). However, not all SMT assembly lines are created equal. Depending on your production needs, different types of SMT assembly lines can be employed to optimize efficiency and output. In this blog, we will explore the key components of an SMT assembly line, the various types of SMT assembly lines, the SMT process, and how to choose the right one for you.

Basic Components in an SMT Assembly Line
An SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly line consists of several critical components, each playing a vital role in manufacturing. The usage of these machines varies depending on the volume of manufacturing. Below is a brief overview of these components
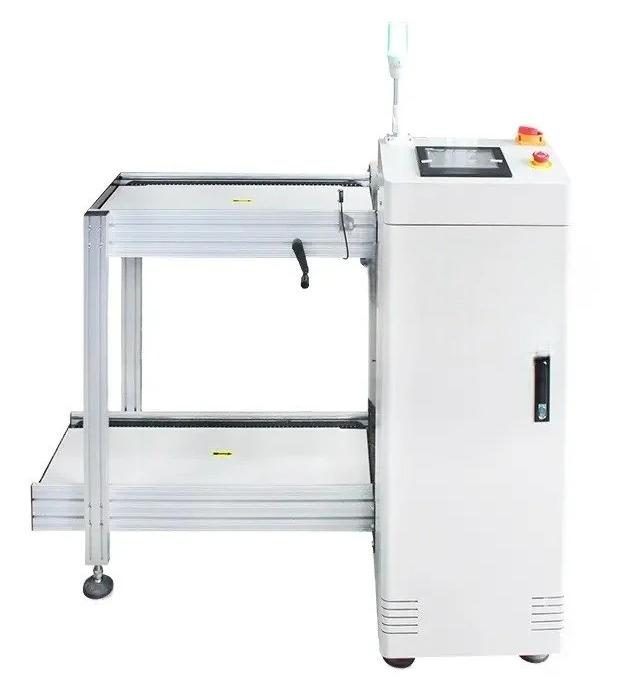

Loader
- Automation: The loader can be fully automated, ensuring a continuous and steady supply of PCBs to the assembly line.
- Capacity: Loaders can handle multiple PCBs simultaneously, depending on the production volume and speed requirements.
- Types: There are various types of loaders, including single-magazine loaders and multi-magazine loaders, tailored to different production needs.

Solder Paste Printer
In higher-volume SMT lines, the loader is followed by the solder paste printer. The solder paste printer applies a thin layer of solder paste onto the PCB's surface at the locations where components will be placed. This paste helps to hold the components in place temporarily and, when heated in a reflow oven, forms permanent solder joints that electrically and mechanically bond the components to the PCB.
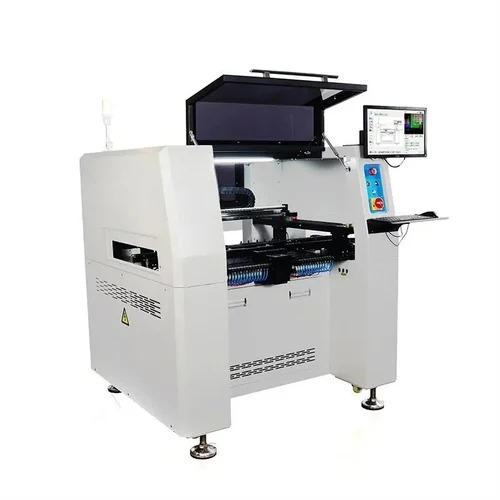

Pick and Place Machine
This machine is central to the SMT process. It picks electronic components from feeders using a vacuum nozzle or mechanical gripper and places them onto the PCB according to programmed data. The precision of this process is enhanced by a vision system that verifies component type, orientation, and placement accuracy. The machine operates at high speeds, performing thousands of pick-and-place actions per hour for efficient PCB production.
- Vacuum Nozzle/Gripper: Picks components from feeder trays or tapes.
- Vision System: Equipped with cameras to check and correct placement in real-time, ensuring high accuracy.
- High-Speed Operation: Can perform thousands of pick-and-place actions per hour, drastically improving production speed.
- Software Integration: Uses CAD data to guide the placement of components, ensuring each element is correctly positioned.

Reflow Oven
The reflow oven is essential for soldering the placed components onto the PCB. It has multiple zones (typically four: preheat, soak, reflow, and cool) that precisely control the temperature to follow a specific soldering profile. This process ensures the proper attachment of components and the formation of reliable solder joints.
- Preheat Zone: Gradually increases the temperature of the PCB to prevent thermal shock.
- Soak Zone: Stabilizes the temperature to activate flux and prepare the solder for reflow.
- Reflow Zone: Peaks the temperature to melt the solder paste, creating solid joints.
- Cooling Zone: Gradually reduces the temperature to solidify the solder without causing stress.
- Profile Control: Ensures each PCB is subjected to an optimal thermal profile for consistent solder quality.

Inline Inspection Systems
Inline inspection systems are used in high-volume SMT assembly lines to ensure the quality and accuracy of component placement and soldering. They detect defects early in the production process to prevent faulty products from advancing further down the line.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Uses cameras and image processing software to inspect solder paste application, component placement, and solder joints.
- X-ray Inspection: Utilized for inspecting hidden solder joints and connections, especially in complex or high-density PCBs.
- 3D Inspection: Provides a three-dimensional view of the PCB, allowing for more accurate defect detection.
- Integration: These systems are integrated directly into the assembly line, allowing for continuous monitoring and immediate feedback.
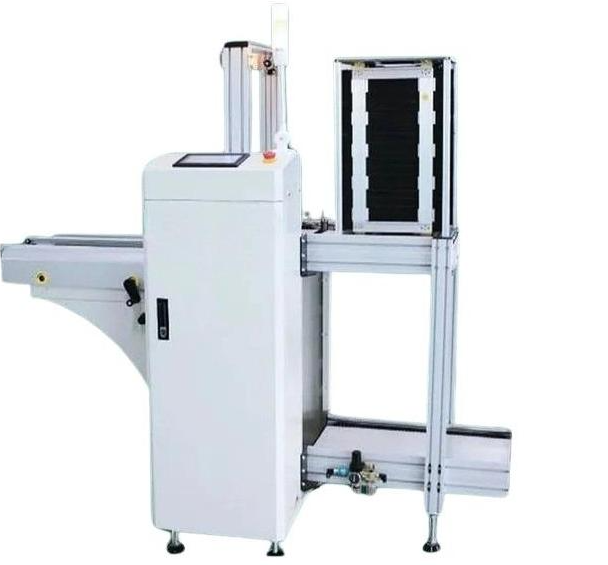

Unloader
The unloader is the final stage in the SMT process.
It uses a controlled mechanism to transfer the finished PCBs from the conveyor belt, ensuring they are collected smoothly and without disruption. Through Controlled Pushing Mechanism it Precisely transfers completed PCBs off the line and Ensures the steady removal of finished boards, preventing bottlenecks and maintaining a continuous production flow.
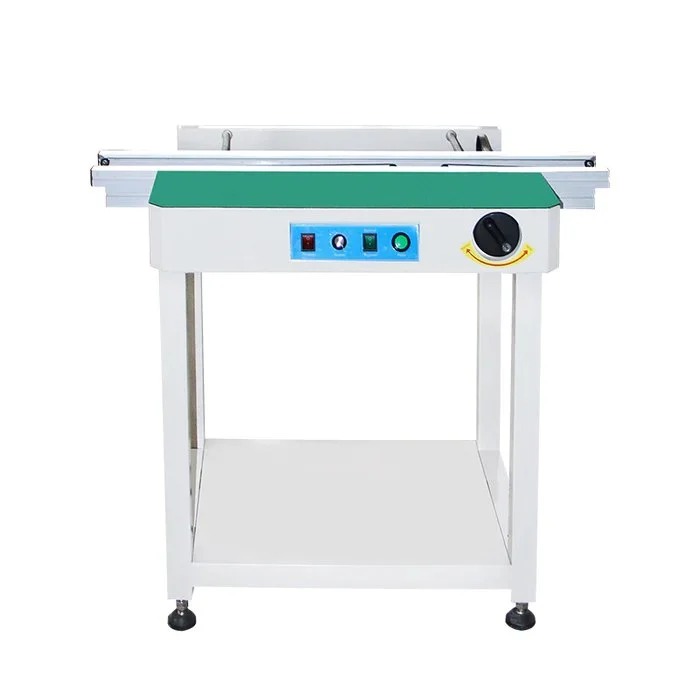

Conveyor Belt
The conveyor belt transfers soldered PCBs from machine to machine, maintaining a continuous and efficient flow throughout the SMT assembly line.

TYPES OF ASSEMBLY LINES
1. Single-Lane SMT Assembly Line
The single-lane SMT assembly line is the most prevalent type, ideal for many small to medium-scale manufacturing operations. Featuring a single conveyor belt, this type moves PCBs through each stage of the assembly process sequentially.
Components:
- Loader
- Conveyor belt
- Pick and place machine
- Reflow oven
- Unloader
2. Dual-Lane SMT Assembly Line
For manufacturers needing higher throughput, the dual-lane SMT assembly line offers a significant efficiency boost.Dual-lane lines have two parallel conveyor belts, allowing the simultaneous processing of two PCBs.
Components:
- Dual loaders
- Dual conveyor belts
- Dual pick and place machines
- Dual reflow ovens
- Dual unloaders
3. Inline SMT Assembly Line
Inline SMT assembly lines are designed for high-volume production, offering a high degree of automation and integration.Equipment is arranged linearly for seamless, automated production.
Components:
- Loader
- Inline solder paste printer
- Inline pick and place machine
- Inline reflow oven
- Inline inspection systems (AOI, X-ray)
- Unloader
4. Prototype SMT Assembly Line
Prototype SMT assembly lines are crucial for developing and testing new products before scaling up to mass production.Tailored for flexibility and precision, these lines are perfect for testing new designs.
Components:
- Precision loaders
- High-precision pick and place machines
- Controlled reflow ovens
- Detailed inspection systems (including manual inspection)
- Manual or semi-automatic unloaders
Selecting the right type of SMT assembly line is crucial for optimizing your manufacturing process. Whether you’re a small-scale manufacturer or a high-volume producer, understanding the capabilities and limitations of each type of assembly line can help you make an informed decision. By choosing the right SMT assembly line, you can enhance efficiency, maintain flexibility, and ensure the production of high-quality electronic products.